Variable costs often fluctuate, and are typically a company’s largest expense. At Business.org, our research is meant to offer general product and service recommendations. We don’t guarantee that our suggestions will work best for each individual or business, so consider your unique needs when choosing products and services. We provide simple, predictable pricing to keep your break-even point analysis accurate and up to date.
Contribution Margin Method (or Unit Cost Basis)
And as much as we think a lower price means more buyers, studies actually show that consumers rely on price to determine the quality of a product or service. Although investors may not be interested in an individual company’s break-even analysis of production, they may use the calculation to determine at what price they will break even on a trade or investment. The calculation is useful when trading in or creating a strategy to buy options or a fixed-income security product.
Situation 2: Inflation-indexed bonds
In terms of its cost structure, the company has fixed costs (i.e., constant regardless of production volume) that amounts to $50k per year. Recall, fixed costs are independent of the sales volume for the given period, and include costs such as the monthly rent, the base employee salaries, and insurance. Your variable costs (or variable expenses) are the expenses that do change with your sales volume. This is the price of raw materials, labor, and distribution for the goods or service you sell. For a coffee shop, the variable costs would be the beans, cups, sleeves, and labor used to produce one cup of coffee.
Benefits of break-even analysis
Determining the number of units that need to be sold to achieve the break-even point is one of the most common methods of break-even analysis. This means Sam’s team needs to sell $2727 worth of Sam’s Silly Soda in that month, to break even. This means Sam needs to sell just over 1800 cans of the new soda in a month, to reach the break-even point. Sales Price per Unit- This is how much a company is going to charge consumers for just one of the products that the calculation is being done for.
- While the breakeven point focuses on financial metrics, successful business decisions also require a holistic view that looks outside the number.
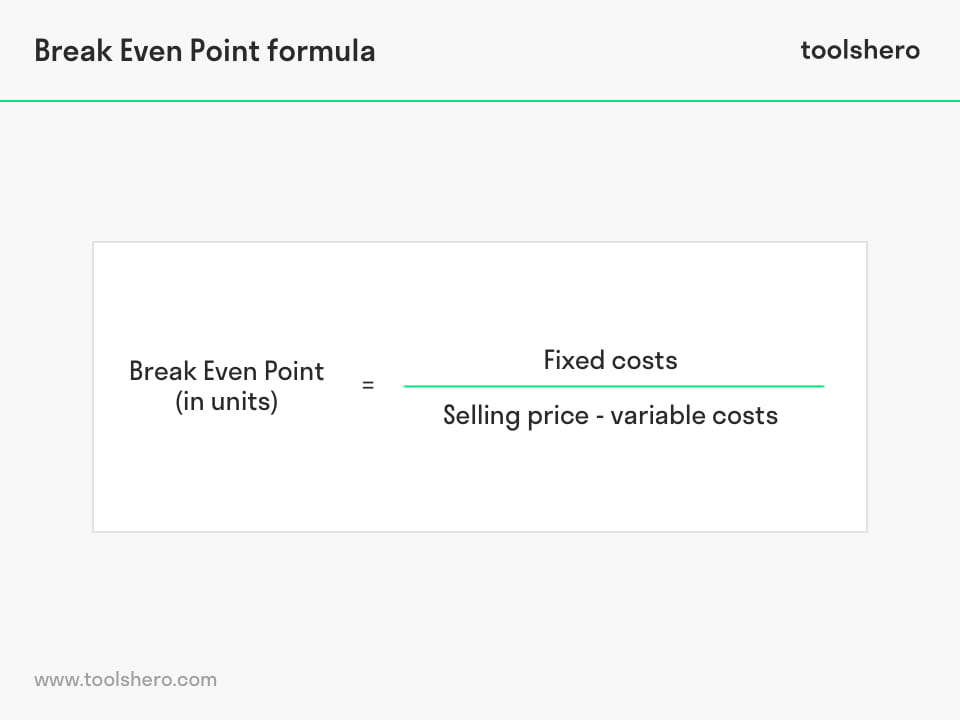
- To find the total units required to break even, divide the total fixed costs by the unit contribution margin.
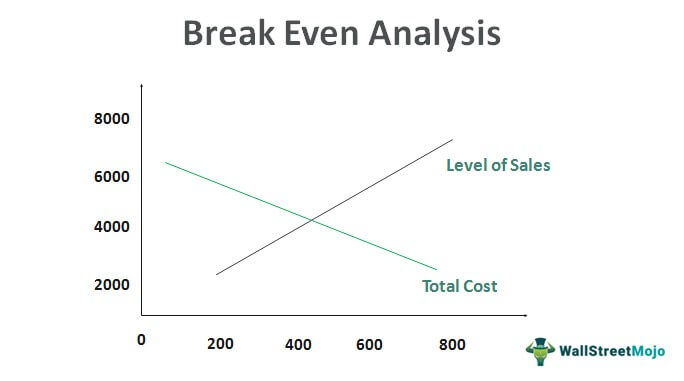
- The Break-Even Point (BEP) is the inflection point at which the revenue output of a company is equal to its total costs and starts to generate a profit.
Break-Even Price: Definition, Examples, and How To Calculate It
Its fixed costsclosefixed costsFixed costs are expenses a business has to pay which do not change with output, eg rent. Financial terms and calculations includes revenue, costs, profits and loss, average rate of return, and break even. Break-even analysis can help determine those answers before you make any big decisions. For example, if the demand for your product is smaller than the number of units you’ll need to sell to breakeven, it may not be worth bringing the product to market at all. Finding your break-even point gives you a better idea of which risks are really worth taking. The break-even point (BEP) is the point at which the costs of running your business equals the amount of revenue generated by your business in a specified period of time.
Also, remember that this analysis doesn’t take into consideration the present vs. future value of your funds. See the time value of money calculator for more information about this topic. In effect, the insights derived from performing break-even analysis enables a company’s management team to set more concrete sales goals since a specific number to target was determined.
In options trading, the break-even price is the price in the underlying asset at which investors can choose to exercise or dispose of the contract without incurring a loss. The result of this calculation is always how many products a business needs to sell in order to break even. The calculation in brackets, which gives the contribution per unit, must be completed first.
Now that we know what break-even analysis consists of, we can begin modeling it in Excel. The two most useful are by creating a break-even calculator or by using Goal Seek, which is a built-in Excel tool. Please note that this can be either per unit or total or expressed as a percentage. To get a better sense of what this all means, let’s take a more detailed look at the formula components. Central to the break-even analysis is the concept of the break-even point (BEP). The following break-even point analysis formulas will help you get there.
He is an expert on personal finance, corporate finance and real estate and has assisted thousands of clients in meeting their financial goals over his career. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
The main thing to understand in managerial accounting is the difference between revenues and profits. Since the expenses are greater than the revenues, these products great a loss—not a profit. DigitalOcean provides straightforward, budget-friendly cloud solutions to lower your xero accounting software blog and news fixed and variable costs. Our products keep your overhead low and operations streamlined, allowing you to scale up or down to cut unnecessary costs and hit your break-even point quicker. If your sales price is too low, you might have to sell too many units to break even.
A breakeven point tells you what price level, yield, profit, or other metric must be achieved not to lose any money—or to make back an initial investment on a trade or project. Thus, if a project costs $1 million to undertake, it would need to generate $1 million in net profits before it breaks even. This $40 reflects the revenue collected to cover the remaining fixed costs, which are excluded when figuring the contribution margin. Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer. The Motley Fool reaches millions of people every month through our premium investing solutions, free guidance and market analysis on Fool.com, top-rated podcasts, and non-profit The Motley Fool Foundation. The variable costsclosevariable costsVariable costs are expenses a business has to pay which change directly with output, eg raw materials.